Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Visualization of discrete-continuous convolutions
In this example, we demonstrate the usage of the discrete-continuous (DISCO) convolutions used in the localized neural operator framework. These modules can be used on both equidistant and unstructured grids.
Preparation
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import math
from functools import partial
from matplotlib import image
from torch_harmonics.quadrature import legendre_gauss_weights, lobatto_weights, clenshaw_curtiss_weights
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cmap="inferno"
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
from neuralop.layers.discrete_continuous_convolution import DiscreteContinuousConv2d, DiscreteContinuousConvTranspose2d, EquidistantDiscreteContinuousConv2d, EquidistantDiscreteContinuousConvTranspose2d
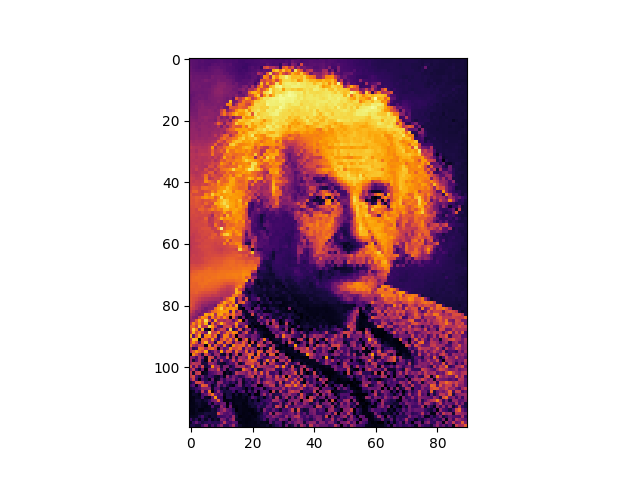
Let’s start by loading an example image
os.system("curl https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d3/Albert_Einstein_Head.jpg/360px-Albert_Einstein_Head.jpg -o ./einstein.jpg")
nx = 90
ny = 120
img = image.imread('./einstein.jpg')
data = nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0), size=(ny,nx)).squeeze()
plt.imshow(data, cmap=cmap)
plt.show()

/home/runner/work/neuraloperator/neuraloperator/examples/plot_DISCO_convolutions.py:40: UserWarning: The given NumPy array is not writable, and PyTorch does not support non-writable tensors. This means writing to this tensor will result in undefined behavior. You may want to copy the array to protect its data or make it writable before converting it to a tensor. This type of warning will be suppressed for the rest of this program. (Triggered internally at ../torch/csrc/utils/tensor_numpy.cpp:206.)
data = nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0), size=(ny,nx)).squeeze()
Let’s create a grid on which the data lives
x_in = torch.linspace(0, 2, nx)
y_in = torch.linspace(0, 3, ny)
x_in, y_in = torch.meshgrid(x_in, y_in)
grid_in = torch.stack([x_in.reshape(-1), y_in.reshape(-1)])
# compute the correct quadrature weights
# IMPORTANT: this needs to be done right in order for the DISCO convolution to be normalized proeperly
w_x = 2*torch.ones_like(x_in) / nx
w_y = 3*torch.ones_like(y_in) / ny
q_in = (w_x * w_y).reshape(-1)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.1/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/torch/functional.py:534: UserWarning: torch.meshgrid: in an upcoming release, it will be required to pass the indexing argument. (Triggered internally at ../aten/src/ATen/native/TensorShape.cpp:3595.)
return _VF.meshgrid(tensors, **kwargs) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
Visualize the grid
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.scatter(grid_in[0], grid_in[1], s=0.2)
plt.xlim(0,2)
plt.ylim(0,3)
plt.show()
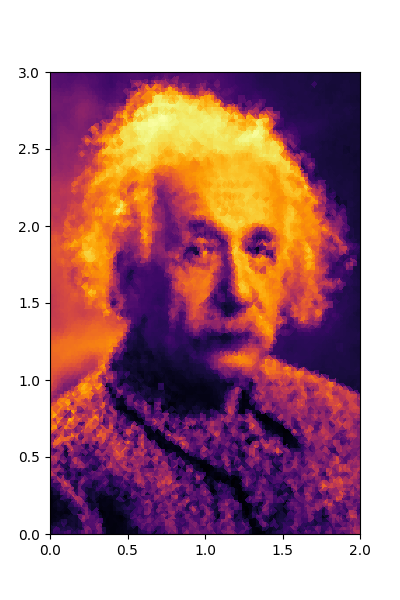
Format data into the same format and plot it on the grid
data = data.permute(1,0).flip(1).reshape(-1)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.tripcolor(grid_in[0], grid_in[1], data, cmap=cmap)
# plt.colorbar()
plt.xlim(0,2)
plt.ylim(0,3)
plt.show()

For the convolution output we require an output mesh
nxo = 90
nyo = 120
x_out = torch.linspace(0, 2, nxo)
y_out = torch.linspace(0, 3, nyo)
x_out, y_out = torch.meshgrid(x_out, y_out)
grid_out = torch.stack([x_out.reshape(-1), y_out.reshape(-1)])
# compute the correct quadrature weights
w_x = 2*torch.ones_like(x_out) / nxo
w_y = 3*torch.ones_like(y_out) / nyo
q_out = (w_x * w_y).reshape(-1)
Initialize the convolution and set the weights to something resembling an edge filter/finit differences
conv = DiscreteContinuousConv2d(1, 1, grid_in=grid_in, grid_out=grid_out, quadrature_weights=q_in, kernel_shape=[2,4], radius_cutoff=5/nyo, periodic=False).float()
# initialize a kernel resembling an edge filter
w = torch.zeros_like(conv.weight)
w[0,0,1] = 1.0
w[0,0,3] = -1.0
conv.weight = nn.Parameter(w)
psi = conv.get_local_filter_matrix()
in order to compute the convolved image, we need to first bring it into the right shape with batch_size x n_channels x n_grid_points
out = conv(data.reshape(1, 1, -1))
print(out.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.imshow(torch.flip(out.squeeze().detach().reshape(nxo, nyo).transpose(0,1), dims=(-2, )), cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
out1 = torch.flip(out.squeeze().detach().reshape(nxo, nyo).transpose(0,1), dims=(-2, ))
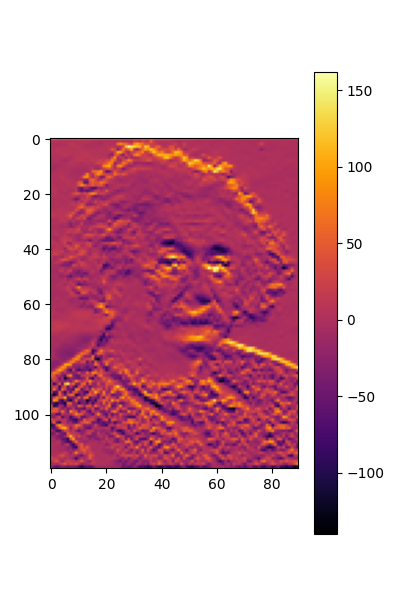
torch.Size([1, 1, 10800])
conv_equi = EquidistantDiscreteContinuousConv2d(1, 1, (nx, ny), (nxo, nyo), kernel_shape=[2,4], radius_cutoff=5/nyo, domain_length=[2,3])
# initialize a kernel resembling an edge filter
w = torch.zeros_like(conv.weight)
w[0,0,1] = 1.0
w[0,0,3] = -1.0
conv_equi.weight = nn.Parameter(w)
data = nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0), size=(ny,nx)).float()
out_equi = conv_equi(data)
print(out_equi.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.imshow(out_equi.squeeze().detach(), cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
out2 = out_equi.squeeze().detach()
print(out2.shape)
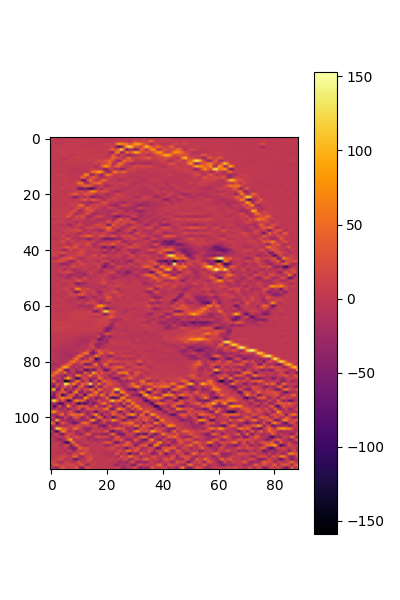
torch.Size([1, 1, 119, 89])
torch.Size([119, 89])
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.imshow(conv_equi.get_local_filter_matrix()[0].detach(), cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar()
# # %%
# print("plt the error:")
# plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
# plt.imshow(out1 - out2, cmap=cmap)
# plt.colorbar()
# plt.show()
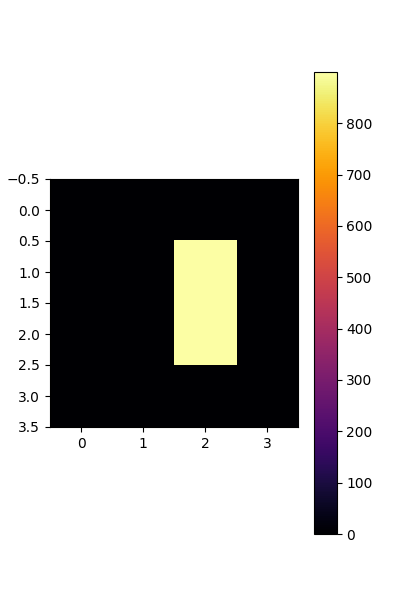
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar object at 0x7fb4c233ca50>
convt = DiscreteContinuousConvTranspose2d(1, 1, grid_in=grid_out, grid_out=grid_in, quadrature_weights=q_out, kernel_shape=[2,4], radius_cutoff=3/nyo, periodic=False).float()
# initialize a flat
w = torch.zeros_like(conv.weight)
w[0,0,0] = 1.0
w[0,0,1] = 1.0
w[0,0,2] = 1.0
w[0,0,3] = 1.0
convt.weight = nn.Parameter(w)
data = nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0), size=(ny,nx)).squeeze().float().permute(1,0).flip(1).reshape(-1)
out = convt(data.reshape(1, 1, -1))
print(out.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.imshow(torch.flip(out.squeeze().detach().reshape(nx, ny).transpose(0,1), dims=(-2, )), cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
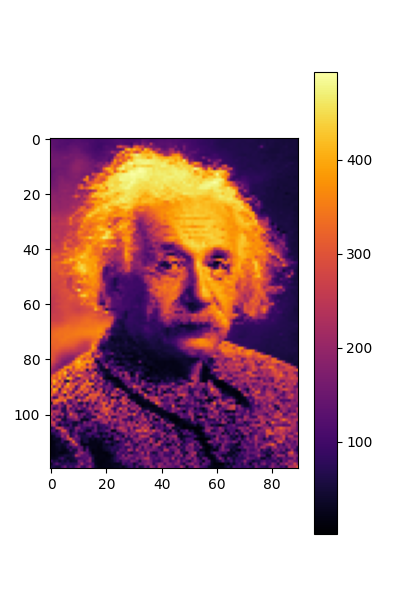
torch.Size([1, 1, 10800])
convt_equi = EquidistantDiscreteContinuousConvTranspose2d(1, 1, (nxo, nyo), (nx, ny), kernel_shape=[2,4], radius_cutoff=3/nyo, domain_length=[2,3])
# initialize a flat
w = torch.zeros_like(convt_equi.weight)
w[0,0,0] = 1.0
w[0,0,1] = 1.0
w[0,0,2] = 1.0
w[0,0,3] = 1.0
convt_equi.weight = nn.Parameter(w)
data = nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0), size=(nyo,nxo)).float()
out_equi = convt_equi(data)
print(out_equi.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6), )
plt.imshow(out_equi.squeeze().detach(), cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
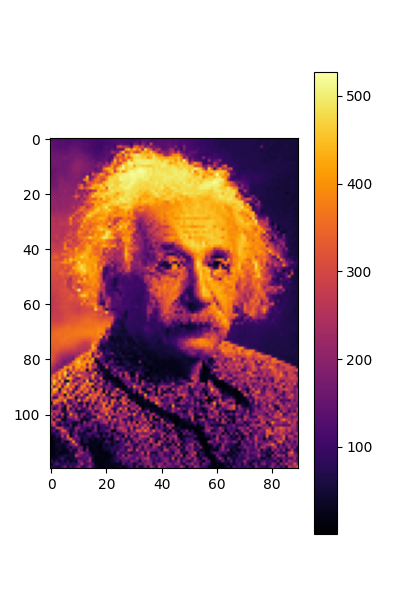
torch.Size([1, 1, 120, 90])
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 31.267 seconds)