Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
U-NO on Darcy-Flow
Training a U-shaped Neural Operator (U-NO) on the small Darcy-Flow example we ship with the package.
This tutorial demonstrates the U-NO architecture, which combines the resolution invariance of neural operators with the multi-scale feature extraction of U-Net architectures. The U-NO uses skip connections and multi-resolution processing to capture both local and global features in the data, making it particularly effective for complex PDE problems.
Import dependencies
We import the necessary modules for working with the UNO model
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from neuralop.models import UNO
from neuralop import Trainer
from neuralop.training import AdamW
from neuralop.data.datasets import load_darcy_flow_small
from neuralop.utils import count_model_params
from neuralop import LpLoss, H1Loss
device = "cpu"
Loading the Darcy-Flow dataset
We load the Darcy-Flow dataset for training and testing.
train_loader, test_loaders, data_processor = load_darcy_flow_small(
n_train=1000,
batch_size=32,
n_tests=[100, 50],
test_resolutions=[16, 32],
test_batch_sizes=[32, 32],
)
Loading test db for resolution 16 with 100 samples
Loading test db for resolution 32 with 50 samples
Creating the U-NO model
We create a U-shaped Neural Operator with the following architecture:
in_channels: Number of input channels
out_channels: Number of output channels
hidden_channels: Width of the hidden layers
uno_out_channels: Channel dimensions for each layer in the U-Net structure
uno_n_modes: Fourier modes for each layer (decreasing then increasing)
uno_scalings: Scaling factors for each layer
model = UNO(
in_channels=1,
out_channels=1,
hidden_channels=64,
projection_channels=64,
uno_out_channels=[32, 64, 64, 64, 32],
uno_n_modes=[[8, 8], [8, 8], [4, 4], [8, 8], [8, 8]],
uno_scalings=[[1.0, 1.0], [0.5, 0.5], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1, 1]],
horizontal_skips_map=None,
channel_mlp_skip="linear",
n_layers=5,
)
model = model.to(device)
# Count and display the number of parameters
n_params = count_model_params(model)
print(f"\nOur model has {n_params} parameters.")
sys.stdout.flush()
Our model has 1405761 parameters.
Creating the optimizer and scheduler
We use AdamW optimizer with weight decay for regularization
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=8e-3, weight_decay=1e-4)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=30)
Setting up loss functions
We use H1 loss for training and L2 loss for evaluation
l2loss = LpLoss(d=2, p=2)
h1loss = H1Loss(d=2)
train_loss = h1loss
eval_losses = {"h1": h1loss, "l2": l2loss}
Displaying configuration
We print the model architecture, optimizer, scheduler, and loss functions
print("\n### MODEL ###\n", model)
print("\n### OPTIMIZER ###\n", optimizer)
print("\n### SCHEDULER ###\n", scheduler)
print("\n### LOSSES ###")
print(f"\n * Train: {train_loss}")
print(f"\n * Test: {eval_losses}")
sys.stdout.flush()
### MODEL ###
UNO(
(positional_embedding): GridEmbeddingND()
(lifting): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(3, 256, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(256, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
(fno_blocks): ModuleList(
(0): FNOBlocks(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): SpectralConv(
(weight): DenseTensor(shape=torch.Size([64, 32, 8, 5]), rank=None)
)
)
(fno_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(64, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(channel_mlp): ModuleList(
(0): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(32, 16, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(16, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
(channel_mlp_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(64, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
)
(1): FNOBlocks(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): SpectralConv(
(weight): DenseTensor(shape=torch.Size([32, 64, 8, 5]), rank=None)
)
)
(fno_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(channel_mlp): ModuleList(
(0): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(64, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
(channel_mlp_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
)
(2): FNOBlocks(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): SpectralConv(
(weight): DenseTensor(shape=torch.Size([64, 64, 4, 3]), rank=None)
)
)
(fno_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(channel_mlp): ModuleList(
(0): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(64, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
(channel_mlp_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
)
(3): FNOBlocks(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): SpectralConv(
(weight): DenseTensor(shape=torch.Size([128, 64, 8, 5]), rank=None)
)
)
(fno_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(128, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(channel_mlp): ModuleList(
(0): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(64, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
(channel_mlp_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(128, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
)
(4): FNOBlocks(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): SpectralConv(
(weight): DenseTensor(shape=torch.Size([96, 32, 8, 5]), rank=None)
)
)
(fno_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(96, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(channel_mlp): ModuleList(
(0): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(32, 16, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(16, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
(channel_mlp_skips): ModuleList(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(96, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
)
)
(horizontal_skips): ModuleDict(
(0): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
(1): Flattened1dConv(
(conv): Conv1d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,), bias=False)
)
)
(projection): ChannelMLP(
(fcs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
(1): Conv1d(64, 1, kernel_size=(1,), stride=(1,))
)
)
)
### OPTIMIZER ###
AdamW (
Parameter Group 0
betas: (0.9, 0.999)
correct_bias: True
eps: 1e-06
initial_lr: 0.008
lr: 0.008
weight_decay: 0.0001
)
### SCHEDULER ###
<torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR object at 0x7fb87ef4c590>
### LOSSES ###
* Train: <neuralop.losses.data_losses.H1Loss object at 0x7fb87ef4c830>
* Test: {'h1': <neuralop.losses.data_losses.H1Loss object at 0x7fb87ef4c830>, 'l2': <neuralop.losses.data_losses.LpLoss object at 0x7fb87ef4c6e0>}
Creating the trainer
We create a Trainer object that handles the training loop for the U-NO
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
n_epochs=30,
device=device,
data_processor=data_processor,
wandb_log=False, # Disable Weights & Biases logging
eval_interval=5, # Evaluate every 5 epochs
use_distributed=False, # Single GPU/CPU training
verbose=True,
) # Print training progress
Training the U-NO model
We train the model on our Darcy-Flow dataset. The trainer will:
Run the forward pass through the U-NO
Compute the H1 loss
Backpropagate and update weights
Evaluate on test data every 5 epochs
trainer.train(
train_loader=train_loader,
test_loaders=test_loaders,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
regularizer=False,
training_loss=train_loss,
eval_losses=eval_losses,
)
Training on 1000 samples
Testing on [50, 50] samples on resolutions [16, 32].
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/torch/utils/data/dataloader.py:1118: UserWarning: 'pin_memory' argument is set as true but no accelerator is found, then device pinned memory won't be used.
super().__init__(loader)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.13.11/x64/lib/python3.13/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py:1787: UserWarning: UNO.forward() received unexpected keyword arguments: ['y']. These arguments will be ignored.
return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
Raw outputs of shape torch.Size([32, 1, 16, 16])
/home/runner/work/neuraloperator/neuraloperator/neuralop/training/trainer.py:536: UserWarning: H1Loss.__call__() received unexpected keyword arguments: ['x']. These arguments will be ignored.
loss += training_loss(out, **sample)
[0] time=4.18, avg_loss=0.6413, train_err=20.0396
/home/runner/work/neuraloperator/neuraloperator/neuralop/training/trainer.py:581: UserWarning: LpLoss.__call__() received unexpected keyword arguments: ['x']. These arguments will be ignored.
val_loss = loss(out, **sample)
Eval: 16_h1=0.4022, 16_l2=0.2731, 32_h1=0.6125, 32_l2=0.3017
[5] time=4.12, avg_loss=0.2208, train_err=6.9006
Eval: 16_h1=0.2547, 16_l2=0.1777, 32_h1=0.4186, 32_l2=0.2127
[10] time=4.16, avg_loss=0.1816, train_err=5.6739
Eval: 16_h1=0.2441, 16_l2=0.1535, 32_h1=0.4204, 32_l2=0.1916
[15] time=4.12, avg_loss=0.1844, train_err=5.7641
Eval: 16_h1=0.2480, 16_l2=0.1506, 32_h1=0.3855, 32_l2=0.1756
[20] time=4.17, avg_loss=0.1212, train_err=3.7884
Eval: 16_h1=0.2236, 16_l2=0.1320, 32_h1=0.3791, 32_l2=0.1439
[25] time=4.16, avg_loss=0.0990, train_err=3.0922
Eval: 16_h1=0.1977, 16_l2=0.1096, 32_h1=0.3933, 32_l2=0.1509
{'train_err': 2.525248534977436, 'avg_loss': 0.08080795311927795, 'avg_lasso_loss': None, 'epoch_train_time': 4.182458043999986}
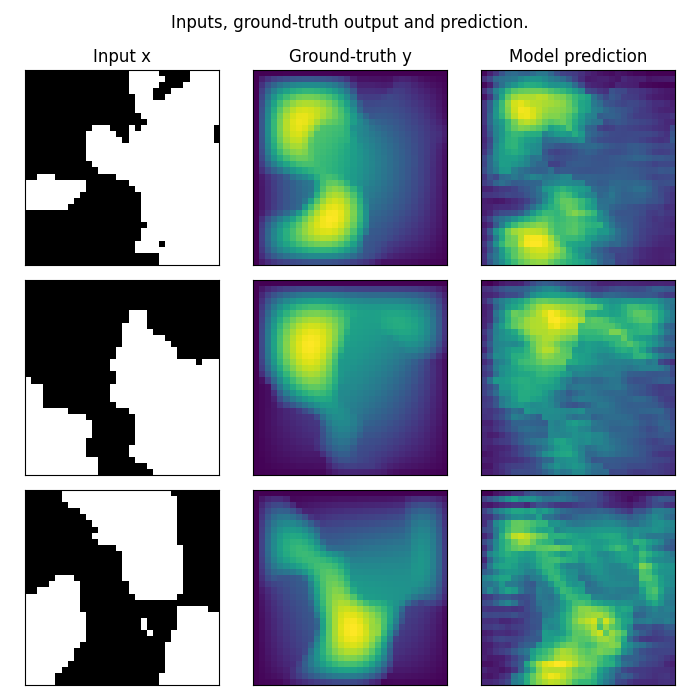
Visualizing U-NO predictions
We visualize the model’s predictions on the Darcy-Flow dataset. Note that we trained on a very small resolution for a very small number of epochs. In practice, we would train at larger resolution on many more samples.
However, for practicality, we created a minimal example that: i) fits in just a few MB of memory ii) can be trained quickly on CPU
In practice we would train a Neural Operator on one or multiple GPUs
test_samples = test_loaders[32].dataset
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7))
for index in range(3):
data = test_samples[index]
data = data_processor.preprocess(data, batched=False)
# Input x
x = data["x"]
# Ground-truth
y = data["y"]
# Model prediction: U-NO output
out = model(x.unsqueeze(0).to(device)).cpu()
# Plot input x
ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 3, index * 3 + 1)
ax.imshow(x[0], cmap="gray")
if index == 0:
ax.set_title("Input x")
plt.xticks([], [])
plt.yticks([], [])
# Plot ground-truth y
ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 3, index * 3 + 2)
ax.imshow(y.squeeze())
if index == 0:
ax.set_title("Ground-truth y")
plt.xticks([], [])
plt.yticks([], [])
# Plot model prediction
ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 3, index * 3 + 3)
ax.imshow(out.squeeze().detach().numpy())
if index == 0:
ax.set_title("U-NO prediction")
plt.xticks([], [])
plt.yticks([], [])
fig.suptitle("U-NO predictions on 32x32 Darcy-Flow data", y=0.98)
plt.tight_layout()
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 9.355 seconds)